Let’s Make Things Happen
“My sales rep at Colorful Packaging was very helpful from start to finish. Our order was completed and shipped quickly. The product was of excellent quality and we will re-order again. I would rate Colorful Packaging as a top supplier.”
George Anderson
Digitalbox CEO

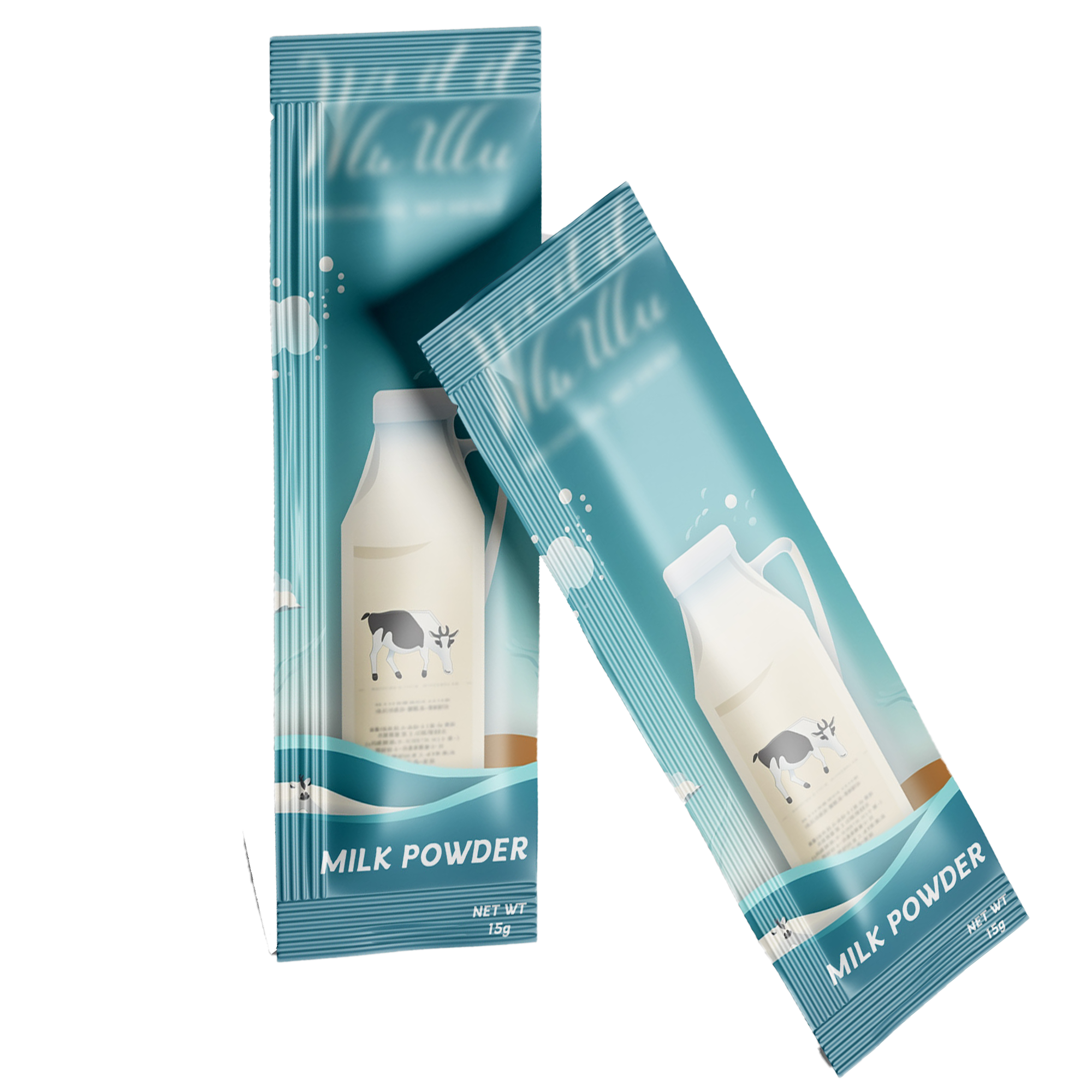
Bag design that inspires
We will provide you with a packaging solution for any type of business. Whether you are designing custom retail packaging with your logo or need custom bags for your e-commerce business, we have a lot of inspiration for your custom product packaging.
More than just a pretty package
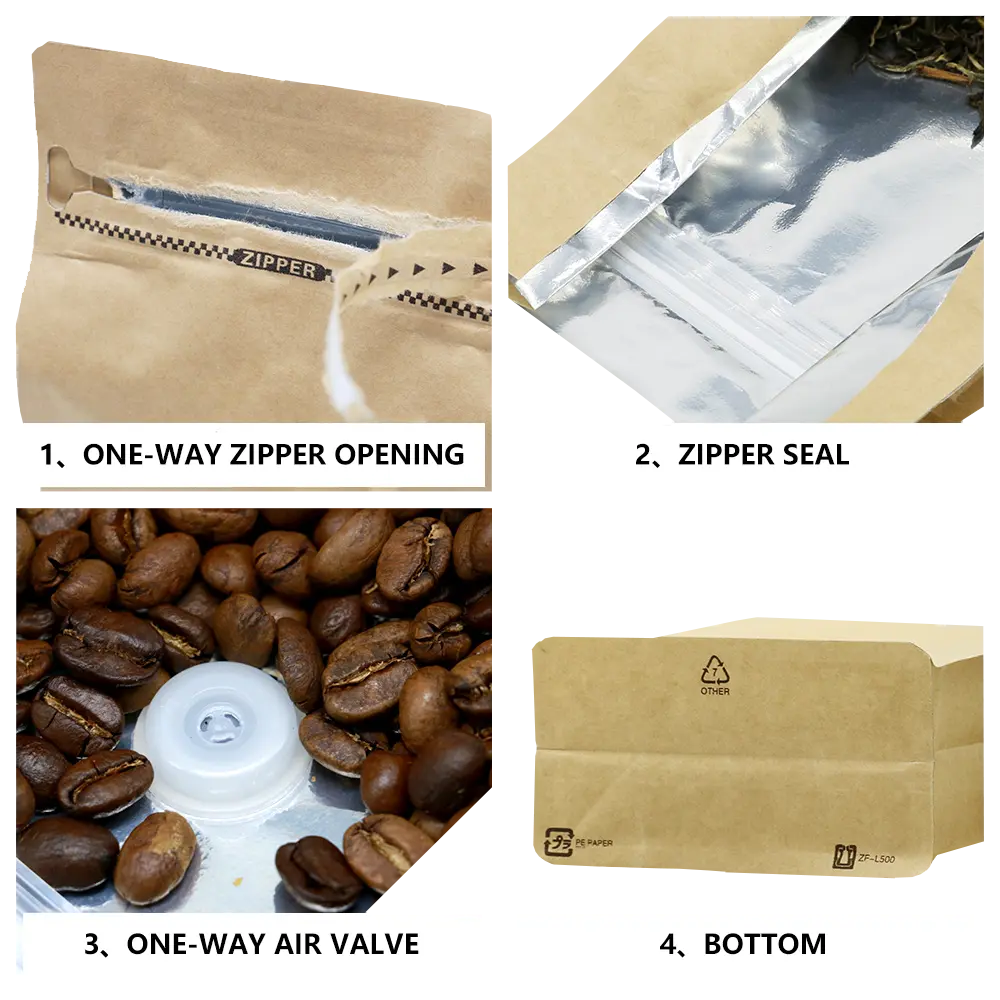
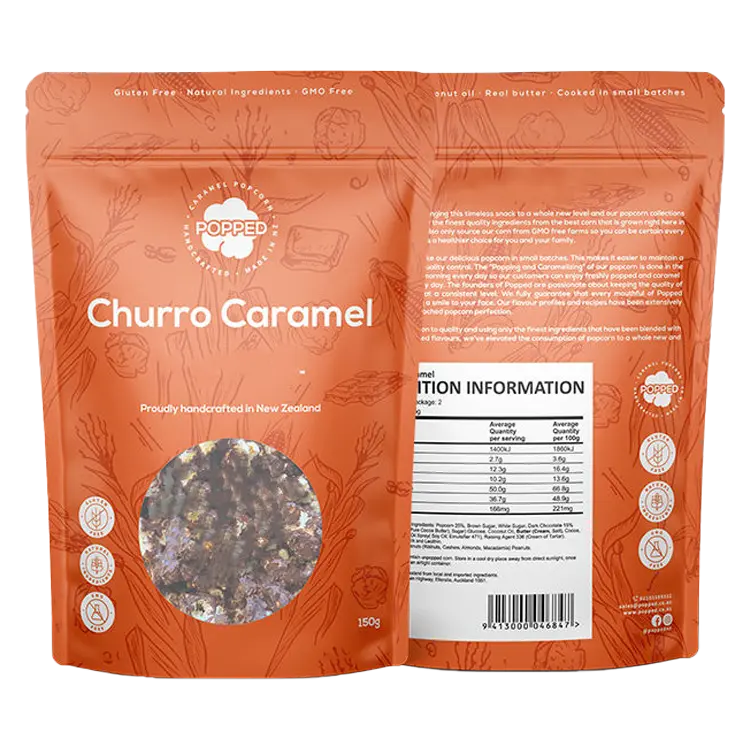
Each of our bespoke bags is designed with your consumers in mind all the way through. In the mail or on display, give your items a unique out-of-the-bag experience. Customized bags made of ecofriendly materials, excellent print quality, and appealing design are what you need for whatever your product’s purpose is. WE CAN CREATE AMAZING PACKAGING FOR YOU – Whatever Your Product’s Use; Business Or Industry
Frequently Asked Questions
Below you’ll find answers to some common questions about creating custom bags. Every order is a little different though, so don’t hesitate to reach out with anything else you might be wondering.
Can I get an instant quote for my order?
Yes, you can select your size, material, and quantity for your project. As you upload artwork, add text, or color the background, you’ll see your Price update in real-time.
What packaging products can I order from Colorfulpackaging?
At Colorfulpackaging, we offer a variety of packages for you to choose from and customize. Our custom packaging bags include Shipping Boxes, Mailer Boxes, and Product Boxes. They can be ordered in both stock and custom sizes at low minimums. These bag styles are perfect for either retail packaging or e-commerce deliveries. Our Mailer Box and Shipping Box cardboard products are safe to mail, while our Product Box packages are intended for display (or to be placed within a shipping-safe box when sent out for delivery). Get started with our packaging bags for your brand today.
What if I’m designing in Adobe Illustrator?
If you’re building your design on one of our Illustrator templates, you can submit your file to us and a quote for your project will be sent to you. You can also email your dieline to our customer support team and we’ll send you back a quote. If you do not have packaging artwork for your bag yet, you can get a rough quote by our customer support team.
What is the turnaround time on my order?
Our Standard turnaround for most custom packaging orders is around 10 business days and Rush turnaround is 7 business days. These turnarounds do not include transit time (15 – 30 business days depending on your location). Special custom or bulk orders may require a few extra days to get set up and produced. Please note that during extremely busy times of the year, some orders may take longer to complete. While delivery estimates cannot be guaranteed, all dates shown at checkout are the quickest estimate we offer. If your delivery date is time sensitive, we highly recommend choosing Rush production and expedited shipping for your bag orders.
What happens after I place my order? Do I get a proof before printing?
After checkout, our dedicated Prepress team will review your design for any technical concerns and send a 2D digital proof of your custom boxes to your email within 24 hours. If any changes need to be made, your bags will start printing.
Will I see proof for my order?
All new orders will receive a digital proof within 24 hours of completing the checkout process.
How do I know if my art is printable?
Our dedicated in-house Prepress team will review your custom bag design for any technical concerns (artwork resolution, blurriness, splits, thin lines, and bleeds) and if found, will note them for your attention in the proof. If you’re unsure of how to fix any printing concerns that are noted, our Prepress representatives are happy to help you through the process. It’s important to keep in mind that our team does not check for spelling or grammar errors, nor do they provide any subjective feedback on design content.
What choices affect my pricing?
As a high-volume producer with scale economies, Colorfulpackaging provides the industry’s most competitive prices on custom-printed bags available. Pricing is generally a factor of five things: dimensions, bag style, ink coverage on the bag, bag material, and quantity (higher quantities = bulk savings). Custom orders of 5,000 or more can be eligible for volume discounts. If you have questions about pricing or choices that can affect your custom packaging order, our customer support team is happy to help!